Advance
This guide explains how to configure upload and download limits for the Ethernet interface on a CE device.
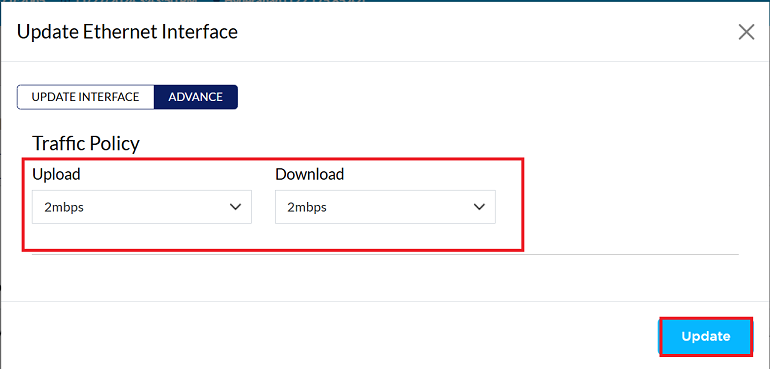
Traffic Policy
-
Navigate to the Login > CE Devices > [Select CE] > Intefaces > [Pick Ethernet Interface] > Edit > Advance.
-
You are in the Advance tab of ethernet interface, find the Traffic Policy section.
-
Set desired Traffic Policy settings to limit upload and download. (i.e. 2Mbps)
-
Click the Update button to save new configuration.
-
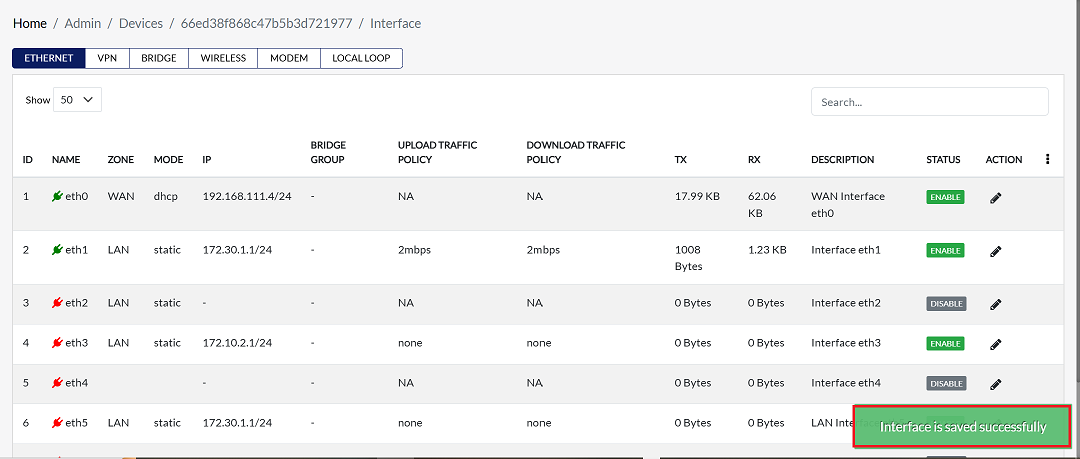
A confirmation message Interface is saved successfully will appear on the screen after successful configuration.
Important Notes for Users
- Traffic Policy limits define the maximum allowed bandwidth. Actual speed may vary depending on ISP plan, network load, and device capability.
- Settings apply only to the selected Ethernet interface. Other interfaces (e.g., Wi-Fi, LTE, VPN) are not affected.
- Ensure correct units (Mbps) are configured to avoid extremely low or high bandwidth allocation.
- Use realistic limits to prevent service interruption or degraded application performance.
- Administrator access is required to modify traffic policy settings.
- Configuration changes apply instantly after clicking Update.
- If unsure about values, contact your network administrator before applying limits.
FAQs
Q:1 What is the purpose of setting upload and download limits on the Ethernet interface?
The main purpose is to control bandwidth usage and ensure fair distribution of network resources. By setting limits, administrators can: Prevent a single device from consuming excessive bandwidth. Guarantee stable performance for critical applications. Apply Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize certain types of traffic. This helps maintain overall network efficiency and avoids congestion.
Q:2 Why am I still experiencing slow speeds even after setting a high traffic policy limit (e.g., 50 Mbps)?
Several factors outside the CE traffic policy can affect speed: ISP Bandwidth Limitations: Your internet plan may not support the configured speed. Network Congestion: Multiple devices using the network simultaneously can reduce available bandwidth. Hardware Limitations: The CE device or client device may not support higher throughput. Cable/Wi-Fi Issues: Faulty Ethernet cables or weak Wi-Fi signals can cause bottlenecks. Background Processes: Other applications or updates are consuming bandwidth in the background. In short, the traffic policy sets a maximum cap, but actual speed depends on external conditions and infrastructure