PBR
This document provides a step-by-step guide on how to configure, edit, and delete Policy-Based Routing (PBR) rules on a CE (Customer Edge) device through its web interface. PBR allows network administrators to define routing policies based on criteria beyond the destination IP address, such as source IP address, source port, destination IP address, destination port, and input interface.
Creating PBR
-
Go to the Login > CE Devices > [Select CE] > ROUTING > PBR > ADD IP Rule.
-
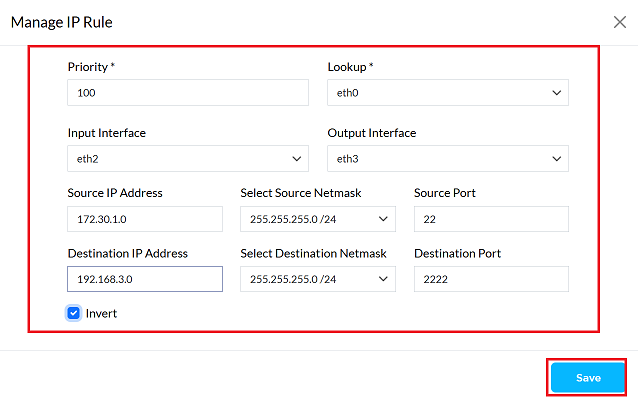
The following parameters need to be configured for the new IP rule:
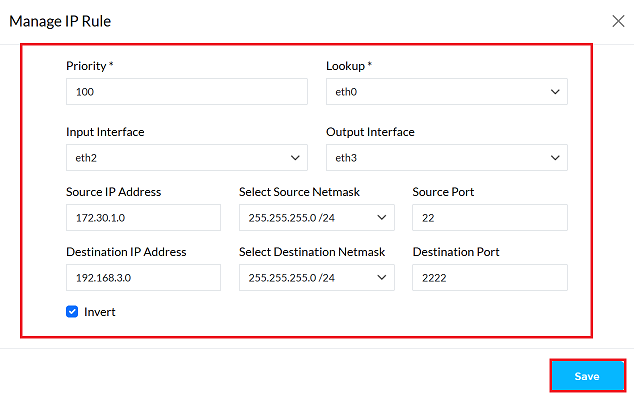
1. Priority:: PBR rules are checked in order of their importance. A lower number indicates a higher importance. The system uses the rule that applies first. Example: 100
2. Lookup: The system determines where the traffic is coming from. This rule will only check traffic coming from that location. Example: eth0
3. Input Interface: Interface where incoming traffic is matched against the rule. Example: eth1
4. Output Interface: An interface used to send out a specific type of traffic. Example: eth2
5. Source IP Address: Using the netmask, you can find a range of IP addresses together with the source IP address. Example: 172.30.1.0
6. Select Source Netmask The netmask, together with the IP address, determines which IP address belongs to which network. Example: 255.255.255.0/24
7. Source Port: Determines which port the traffic originated from, so that it can be identified correctly. Example: 22
8. Destination IP Address: This determines which IP addresses the rule will apply to. Example: 192.168.3.0
9. Select Destination Netmask: Works with destination IP, which determines the list of addresses where data is sent. Example: 255.255.254.0/24
10. Destination Port: Determines which port number data going to a specific location will go to. Example: 2222
11. Invert: If you do not want the rule to apply to certain addresses and ports, you should enable this option. Doing so will cause the rule to apply to all remaining addresses and ports. Action: Check the box to enable inversion.
-
Click the Save button to make the PBR IP rule work on this device.
-
Upon clicking save, a confirmation message IP rule has been created successfully will appear on the screen.
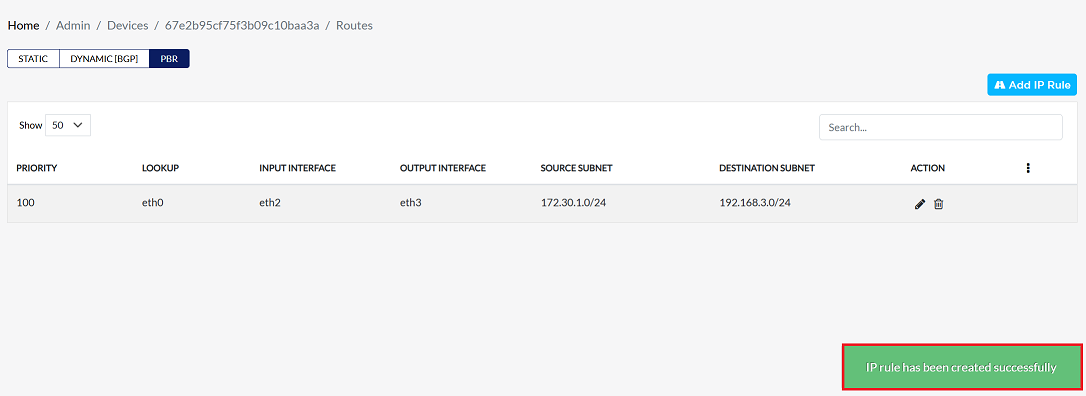
PBR Rule Column grid Fields Details
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Priority | Determines the order of rule evaluation. Lower values have higher priority. |
| Lookup | Specifies the routing table to be used for matching traffic. |
| Input Interface | Interface on which incoming traffic is received and matched against the rule. |
| Output Interface | Interface through which matching traffic will be sent. |
| Source Subnet | Defines the IP address and netmask from where the traffic originates. |
| Destination Subnet | Defines the IP address and netmask to where the traffic is headed. |
| Action | Provides options to edit or delete the IP Rule. |
Editing PBR
To update the details of any PBR, follow these steps:
-
Click on the Edit option in the 'Action' column on the right side of the row of the PBR to be edited.
-
Edit the PBR details as needed. The following details can be updated:
- Priority: The priority can be changed as required. (e.g. 50 out of 100)
- Lookup: The lookup requirement can be changed as required.
- Input interface: The input interface can be changed as required.
- Output interface: The output interface can be changed as required.
- Source IP Address: The source IP address can be changed as required.
- Source Netmask: The source netmask can be changed as required.
- Source Port: The source port can be changed as required.
- Destination IP Address: The destination IP address can be changed as required.
- Destination Netmask: The destination netmask can be changed as required.
- Destination Port: The destination port can be changed as per the requirement.
- Invert: The 'Invert' setting can be changed as per the requirement.
In these changes, the Priority has been changed from 100 to 50. Whereas, no changes have been made in other details such as Lookup, Input Interface, Output Interface, Source IP Address, Source Netmask, Source Port, Destination IP Address, Destination Netmask, Destination Port and Invert, as there is no need to change them.
-
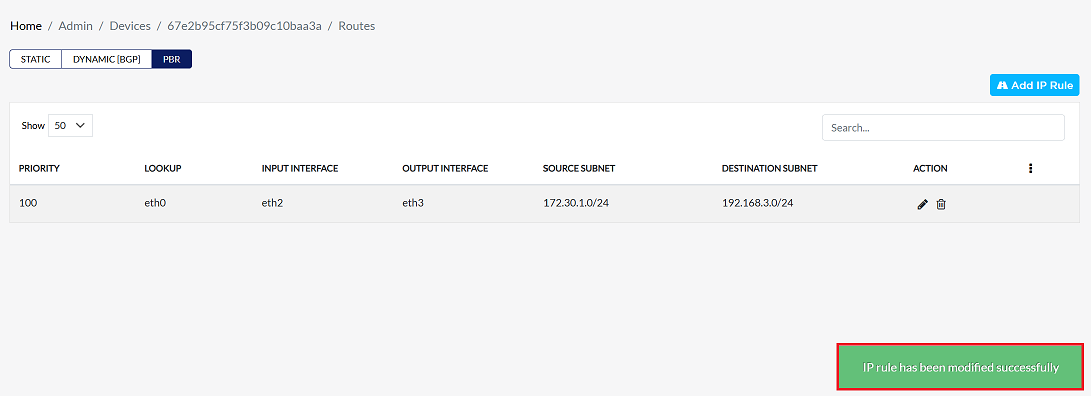
After making all the necessary changes, verify the changes and click on the Save button to apply the updated information.
-
Upon clicking save, a confirmation message IP rule has been modified successfully will appear on the screen.
Deleting PBR
To delete any PBR device, follow these steps:
-
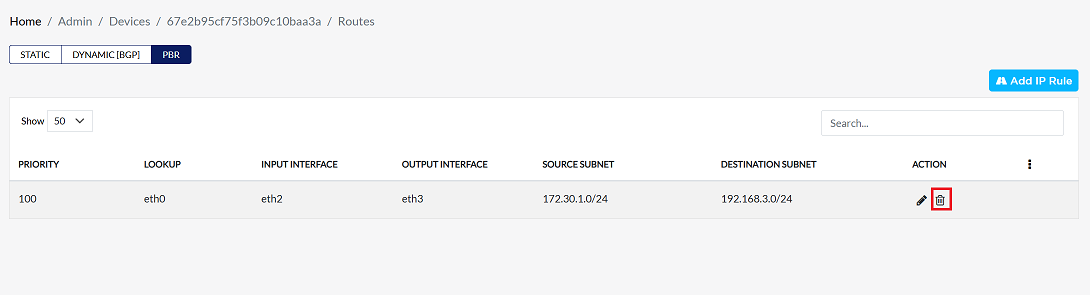
Click on the Delete option in the 'Action' column in the row of the PBR to be deleted.
-
By clicking on the Delete option, a confirmation message popup will open on the screen. This popup asks to confirm the deletion action again, which prevents accidental deletion.
-
The PBR has two options available:
- Confirm Delete: If the PBR really wants to delete the information, click on the Yes button in the popup.
- Cancel Delete: If not intended to delete or clicked by mistake, click on the No button to cancel the action and keep the information safe.
Decision taken in the image As mentioned, the Yes button has been clicked in the image. This means that the deletion action has been confirmed by the PBR and the relevant data will be removed from the system.
-
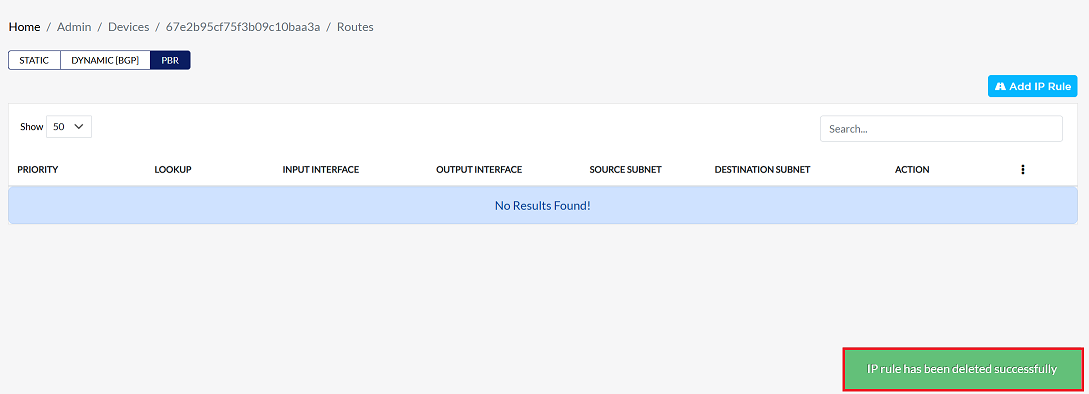
Once deleted, a confirmation message will be displayed IP rules has been deleted successfully.
Example Scenario
Network Setup:
- PC1 has IP: 172.30.1.100
- Router interfaces:
- eth0: main routing table
- eth1: receives traffic from local LAN
- eth2: connects to a VPN
Goal:
Route all SSH traffic (port 22) on the network through PC1 via the VPN (eth2), instead of the main internet link.
PBR Rule Configuration
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Priority | 100 |
| Lookup | eth0 |
| Input Interface | eth1 |
| Output Interface | eth2 |
| Source IP Address | 172.30.1.100 |
| Source Netmask | 255.255.255.0 |
| Source Port | 22 |
| Destination IP | 192.168.3.0 |
| Destination Netmask | 255.255.254.0 |
| Destination Port | 2222 |
| Invert | Unchecked |
Explanation:
When PC1 makes an SSH connection to 192.168.3.0/23 from port 2222, traffic coming on eth1 will go through eth2 (VPN).
Important Notes for Users
- Rule Priority Matters Most: Lower priority values are evaluated first. If multiple rules match the same traffic, the rule with the lowest priority number will be applied.
- Avoid Overlapping Rules: Try not to configure multiple PBR rules that match the same traffic unless absolutely necessary. This helps prevent routing conflicts.
- Check Interface Selection Carefully: Ensure that the Input and Output interfaces are selected correctly. Incorrect interface mapping may cause traffic disruption.
- Use Invert with Caution: Enabling the Invert option reverses the matching logic. Make sure you fully understand its impact before enabling it.
- Always Validate After Saving: After creating or updating a rule, test the traffic flow to confirm that the routing behaviour is as expected.
- Backup Recommended Before Major Changes: If possible, backup or record the existing routing configuration before modifying PBR rules.
- Higher Complexity = Higher Risk: Complex rules involving multiple ports, networks, or inversion settings should be tested carefully to avoid unexpected routing behaviour.
- Ensure Correct Netmask Configuration: Incorrect subnet masks may result in traffic not being matched by the intended rule.
- System Logs Are Useful for Troubleshooting: If traffic is not routing as expected, review the system logs to verify which rule is being applied.
- Admin Permissions Required: Only authorized users with the required access rights should configure, edit, or delete PBR rules.