Diagnostics
The Network Diagnostics Tool makes it easy to check whether the internet connection is working or not. It provides three main functions: Ping, Traceroute, and NSLookup. As a cloud-based feature, there is no need to type commands on a local computer. All checks can be performed directly from the cloud, ensuring a simpler and more convenient process.
Accessing the Diagnostics Tool
- Log in to the account.
- Go to CE Device.
- Select the desired CE Device.
- Click on Diagnostics.
Here is a table summarizing the Diagnostics tool's three key functions:
| Tool | Purpose | Key Use Case | How to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ping | To test connectivity and measure response time. | Checking if a device is online. | Enter an IP address, select Ping, and click START PING. |
| Traceroute | To track the path of data from its source to its destination. | Identifying network bottlenecks or points of failure. | Enter an IP address, select Traceroute, and click START TRACEROUTE. |
| NSLookup | To query the Domain Name System (DNS) for domain and IP mapping. | Verifying that a domain name resolves to the correct IP address. | Enter a domain name, select NSLookup, and click START NSLOOKUP. |
Ping
The Ping utility is used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for messages sent from the source to a destination computer. It helps determine if a device is online and responsive.
Steps to Perform a Ping Test:
-
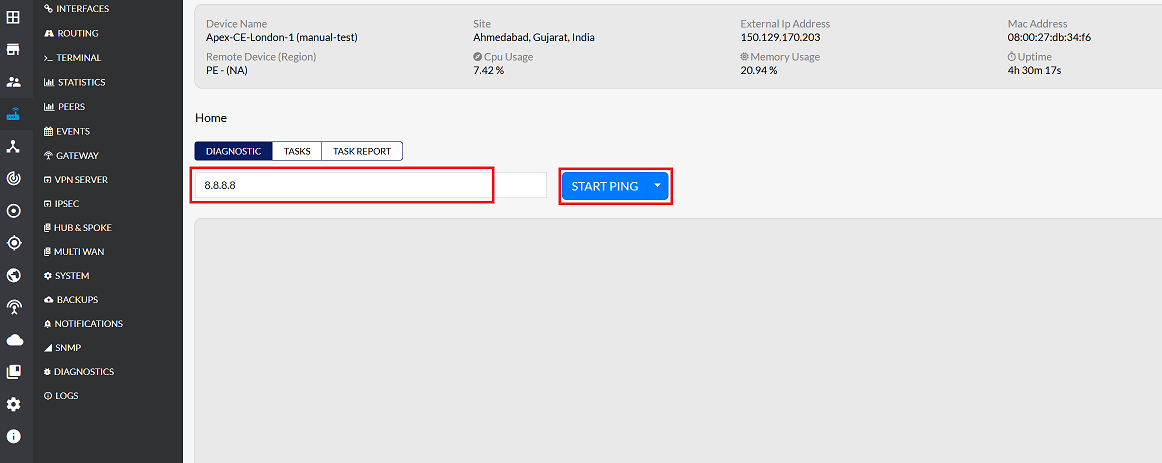
Navigate to the Diagnostics section.
-
In the IP field, enter the desired IP address to test (e.g.,
8.8.8.8). -
From the dropdown menu, select Ping.
-
Click START PING to initiate the test.
-
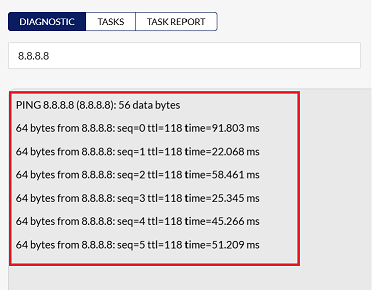
The results, including response times and packet loss, will be displayed.
-
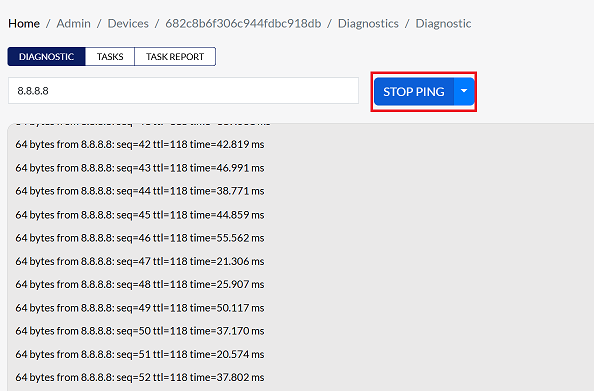
Click STOP PING to end the process once the necessary information is available.
Traceroute
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to track the path of a packet from its source to its destination. It identifies all the intermediate routers and their response times, which is crucial for locating network bottlenecks or points of failure.
Steps to Perform a Traceroute:
-
Navigate to the Diagnostics section.
-
In the IP field, enter the desired IP address to test (e.g.,
8.8.8.8). -
From the dropdown menu, select Traceroute.
-
Click START TRACEROUTE to begin the trace.
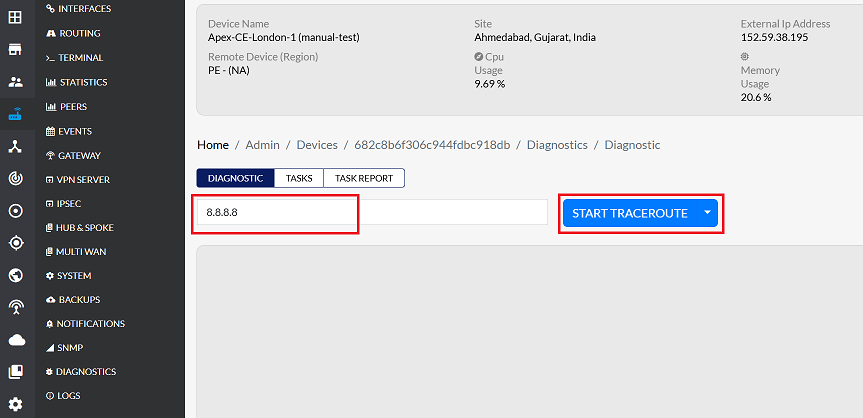
-
The tool will display a list of all the routers and the time taken to reach each one.
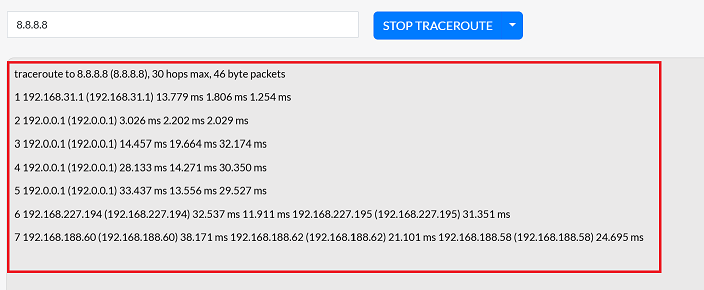
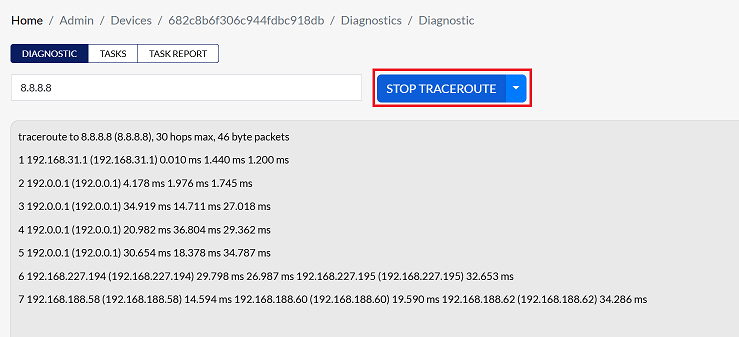
-
Click STOP TRACEROUTE to end the process once the necessary information is available.
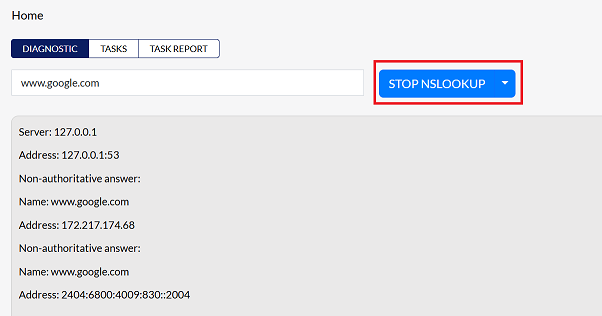
NSLookup
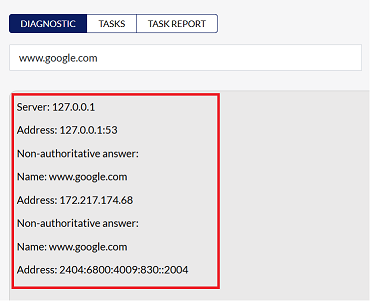
The NSLookup (Name Server Lookup) command-line tool is used to query the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or other DNS records. It's used to verify that a domain name resolves to the correct IP address.
Steps to Perform an NSLookup:
-
Navigate to the Diagnostics section.
-
In the Domain field, enter the domain name to query (e.g.,
www.google.com). -
From the dropdown menu, select NSLookup.
-
Click START NSLOOKUP to initiate the query.
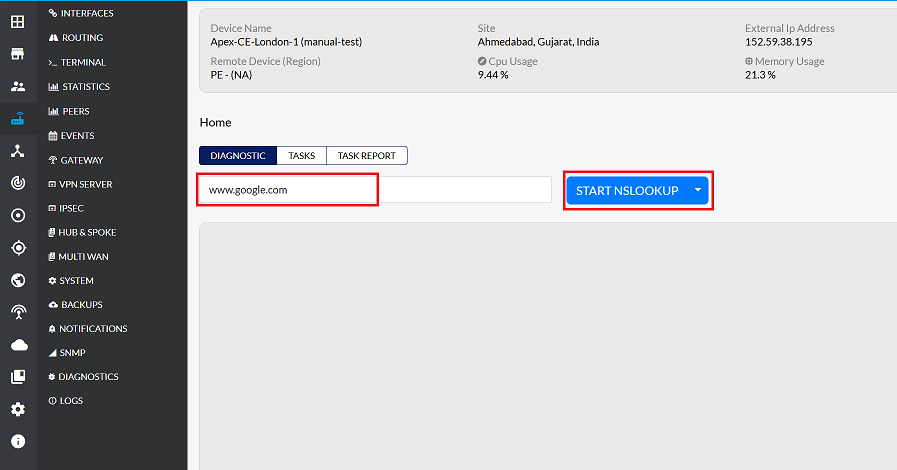
-
The results will show the server, address, and authoritative answers related to the domain name.
-
Click STOP NSLOOKUP when finished.